
Aqua regia separation process of gold and silver alloy Aqua regia is a strong acid solution formed by slowly mixing concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in a volume ratio of 3:1. This solution can effectively dissolve the gold…

925 Silver Electrolytic Purification Solution Silver is a metal with excellent beauty and conductivity, and is widely used in jewelry, electronics and industry. However, the requirements for its purity are different. The purity of traditionally traded silver is 99.99%, and…

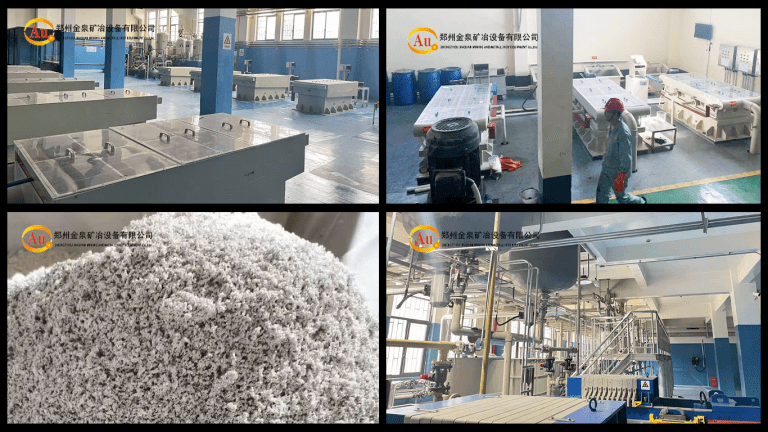
Precious Metal Separation and Comprehensive Refining Project China Hengbang Group recycles and processes a lot of precious metal raw materials. After many discussions with Zhengzhou Jinquan, it chose Zhengzhou Jinquan for project cooperation. The precious metal separation and comprehensive smelting…

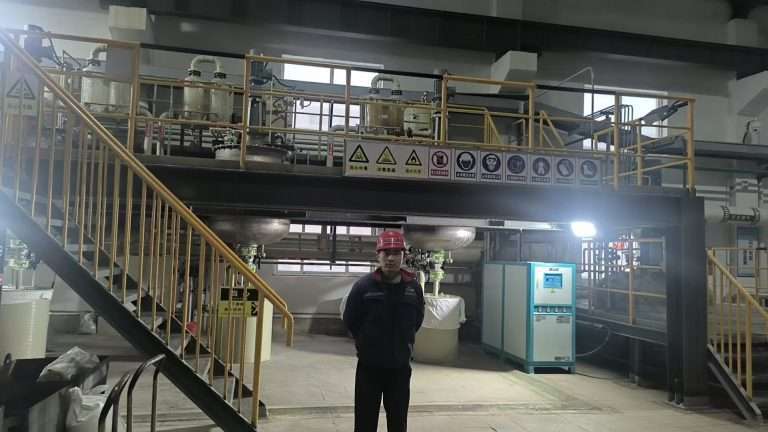
Thailand's silver refining plant put into operation Zhengzhou Jinquan Mining and Metallurgical Equipment Co., Ltd. will undertake the design and installation project of a 500kg/day silver refinery in Thailand in 2024, and will be delivered in December 2024. It took…
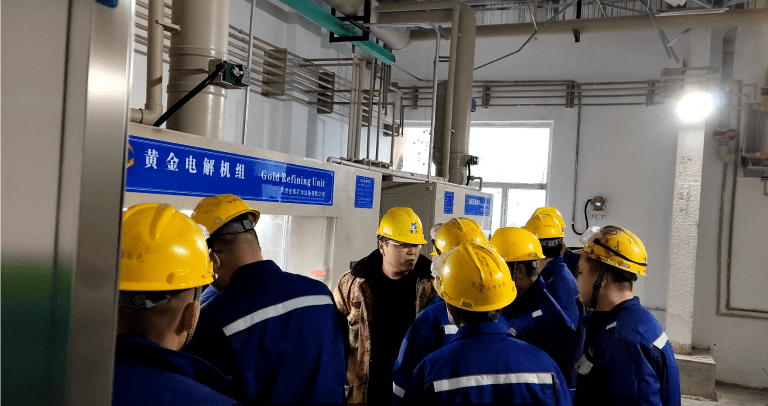

China Qinghai - Gold electrolysis purification project put into production In 2024, after three engineers from Zhengzhou Jinquan Mining Equipment Co., Ltd. stepped up installation and commissioning, they completed the 50kg per…
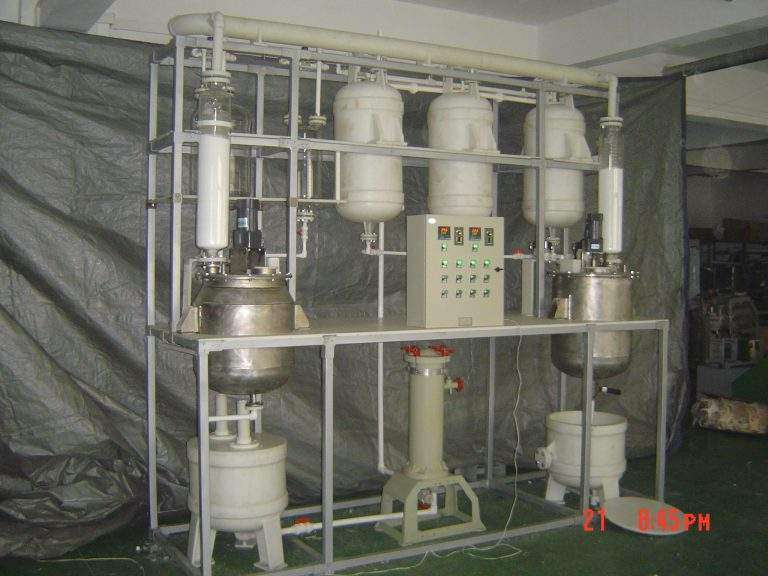

Recycling precious metals (platinum-iridium) from spark plugs Precious metal components in spark plugs Iridium Iridium is usually found at the tip of the center electrode of a spark plug, in the form of a coating or micro-electrode. Its content is…
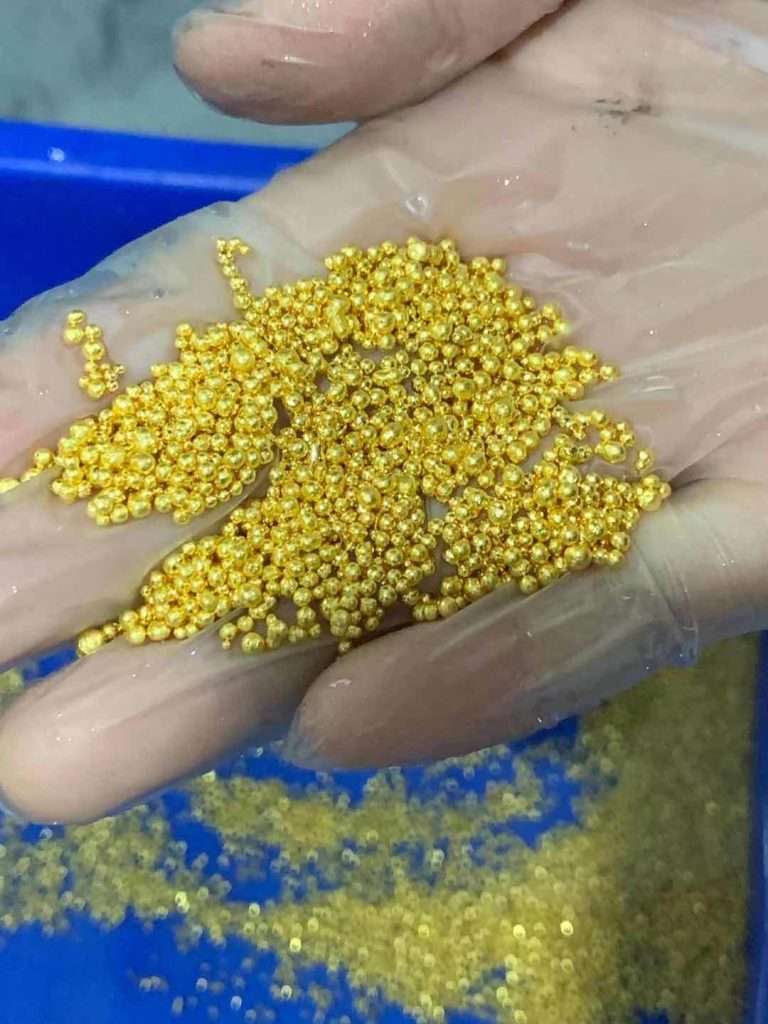

Key technologies for recycling jewelry gold Generally, the purity of recycled jewelry gold is not high. K gold is called gold alloy, so it needs to be processed into 99.99% gold First, jewelry gold needs to be roughly extracted, and…
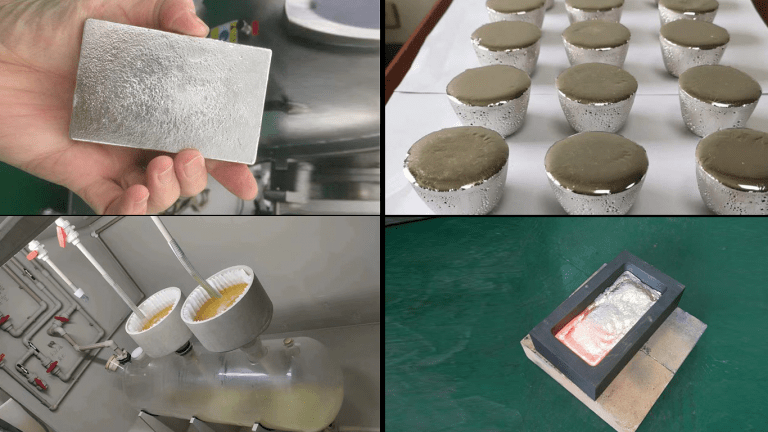

Palladium Carbon Refining Process: Palladium Metal Dissolution Palladium carbon catalysts are commonly used in chemical reactions, especially in organic synthesis and hydrogenation. As electronic waste recycling and precious metal refining continue to grow, the recovery and purification of palladium…
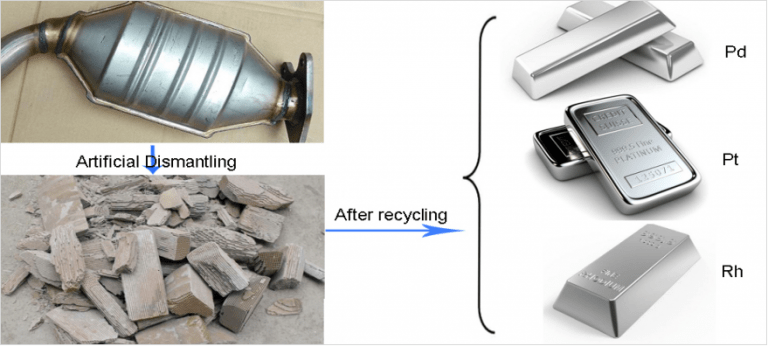
Platinum recovery from platinum catalyst Platinum exists in the form of platinum particles in the catalyst and is widely used in automotive catalysts, chemical reaction catalysts, petroleum refining, etc. 1. Pretreatment of platinum catalyst recovery: First disassemble the shell, then…
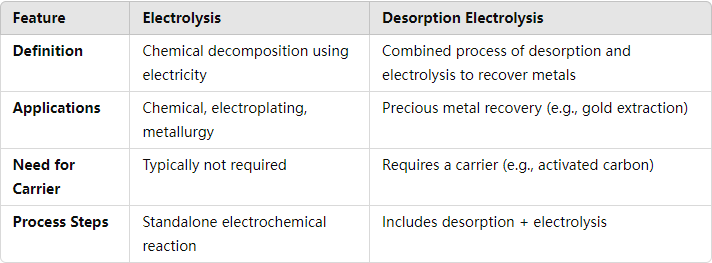
Analysis of the smelter The difference between electrolysis and electrolysis 1.Electrolysis is the process of using electric current to decompose or react chemical substances, which is used to extract metals or separate compounds. 2. Electrolysis is a specific process that…
Benefits of Aqua Regia Gold Purification 1.Aqua Regia has strong oxidizing properties and does not require the addition of a catalyst to react. 2.Aqua Regia can form a soluble chloride complex with gold 3.Aqua Regia is a 1:3 volume ratio…
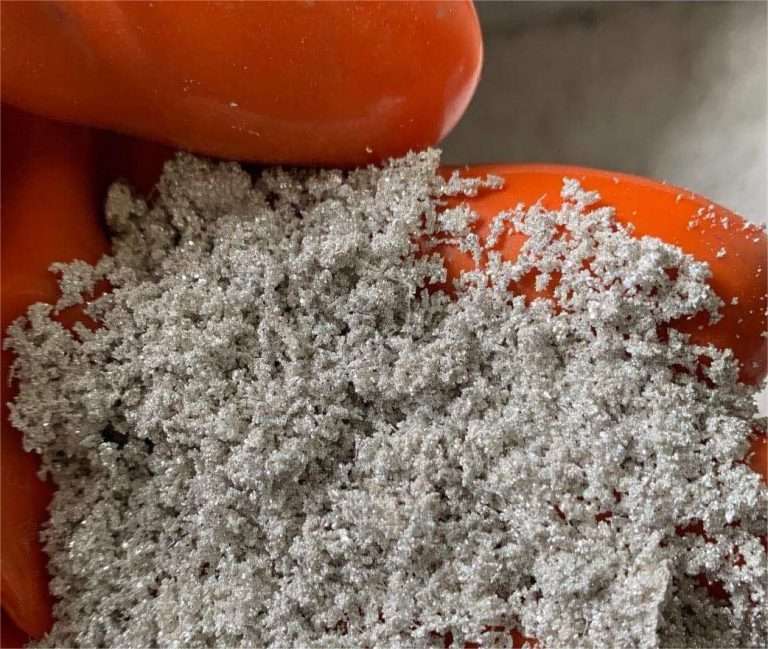

What equipment is best for refining silver nitrate Using electrowinning equipment to extract silver from silver nitrate solution is an effective recovery method. Reduction of silver ions (𝐴𝑔+ ) to metallic silver Cathode reaction (reduction): Ag +e-→ Ag Anode reaction…
Call us now:











